Scientists say there is strong evidence that the Zika virus can be controlled by releasing genetically modified male mosquitoes into the wild so they can mate with the disease-spreading females to produce sterile offspring.
But plans for a trial run in Key Haven, Fla., an unincorporated community just east of Key West, have been so controversial that officials decided to put it to a public vote.
Tuesday’s referendum is non-binding, but will weigh heavily on whether the Florida Keys Mosquito Control District proceeds with the test, which was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in August.
The genetically modified mosquitoes have been tested in Brazil, Panama and the Caymen Islands, where they reduced the wild population of Zika-bearing Aedes aegypti mosquitoes by more than 90 percent, according to British biotechnology company Oxitec, which developed the engineered strain of mosquitoes.
“In comparison, current technologies such as insecticides are only 30-to 50 percent effective at best,” Oxitec spokesman Matthew Warren told Seeker.
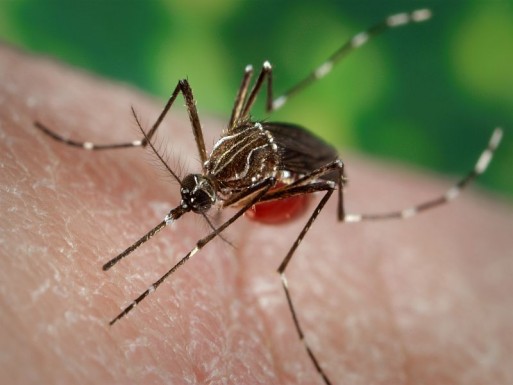
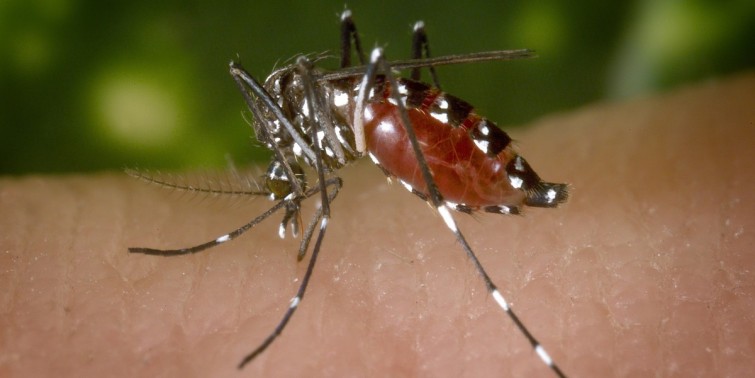
In addition to the Zika virus, which can cause birth defects and other disorders, Aedes aegypti mosquitoes are responsible for the spread of dengue and chikungunya. It’s the female mosquitoes that do the biting, spreading disease in their wake.
Oxitec’s solution is to engineer a gene in the males, which are then released into the wild so they can mate with the females. Any offspring that result from the union will carry an engineered “kill switch” and die before maturing enough to mate or bite, drastically reducing the population.
“We have now released more than 180 million of our male self-limiting mosquitoes worldwide. And there have been no reports of adverse impacts in any of these releases,” Warren said.
The trial in the Florida Keys would be the first in the United States.
“The genetically modified mosquitoes are incredibly promising. They’ve been incredibly successful in many of the cases where they’ve been tested for Zika so far. I think that they have tremendous promise in the United States, but there are obviously a lot of fears,” ecologist Colin Carlson, with the University of California, Berkeley, told Seeker.
Among those opposed to the Florida trial is a group of physicians, led by Dr. John Norris, who have questions about whether Oxitec’s mosquitoes, which are dependent on the antibiotic tetracycline to survive, will end up spreading antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
“We do not know what to expect when millions of mosquitoes are released on small neighborhoods possibly covered in resistant germs,” the doctors wrote in a petition to the Florida Keys Mosquito Control Board.
If the board decides to proceed with the trial, the doctors want to conduct a study to see if residents have altered bacterial resistance patterns.
Whether the referendum passes or not, one thing is certain: the spread of the Zika virus in South Florida is growing.
“We’re still trying to figure out how severe it’s going to be,” Carlson said. “From a public health perspective, it’s not a great situation.”
Pending approval by the Florida Keys Mosquito Control District, Oxitec’s test could begin next year.
Seeker.com